Abstract
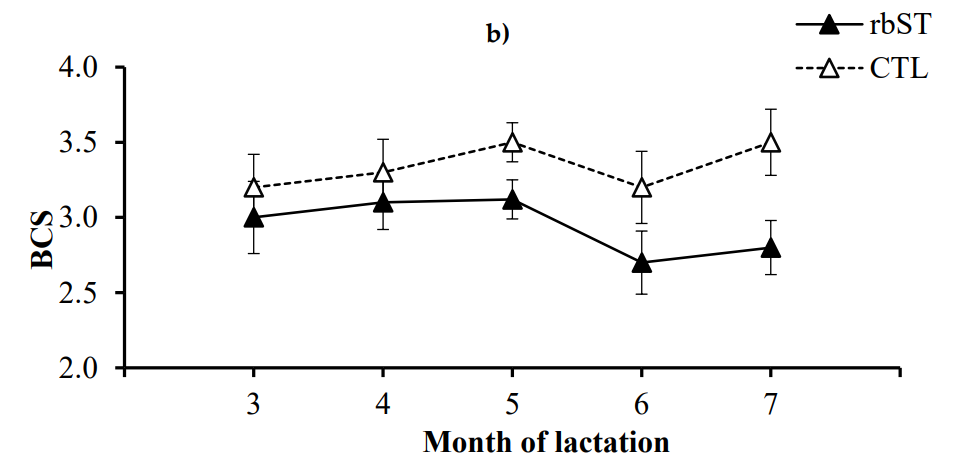
The objective of the current study was to assess the impact of recombinant bovine somatotropin (rbST) on mastitis incidence and body condition score (BCS) in Nili Ravi buffaloes. In a double-blinded clinical trial, 50 buffaloes (primiparous and multiparous) at + 60 days post-calving were divided into treatment (n = 25) and placebo control (n = 25) groups. The treatment group received ten doses of 500 mg rbST with 14-day intervals, while the control group received a placebo with the same regimen. Data on dry matter intake, milk yield and milk composition, mastitis incidence, and body condition score were collected. Repeated measures ANOVA was applied to the weekly averages of milk yield, dry matter intake, and milk composition. Individual incidences of mastitis were recorded throughout the study period. The results revealed that milk production significantly increased in both primiparous and multiparous buffaloes treated with rbST. However, the relative risk of mastitis increased by 3.0 times (95% CI: 1.62-6.88) in the bST-treated group compared to the control, with a 5-fold higher risk of multiple mastitis episodes (95% CI: 1.2–20.6). BCS in primiparous buffaloes was lower in the rbST-treated group, but there was no significant change in BCS dynamics between the rbST and control groups for either primiparous or multiparous buffaloes. These findings suggest that while rbST enhances milk yield in Nili Ravi buffaloes, its use may compromise animal welfare due to increased mastitis risk.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2024 Muhammad Imran, Muhammad Asim Tausif , Muhammad Waseem (Author)